контрактне виробництво
свічки контактне виробництво
виробництво торгова марка
ASKORUTIN
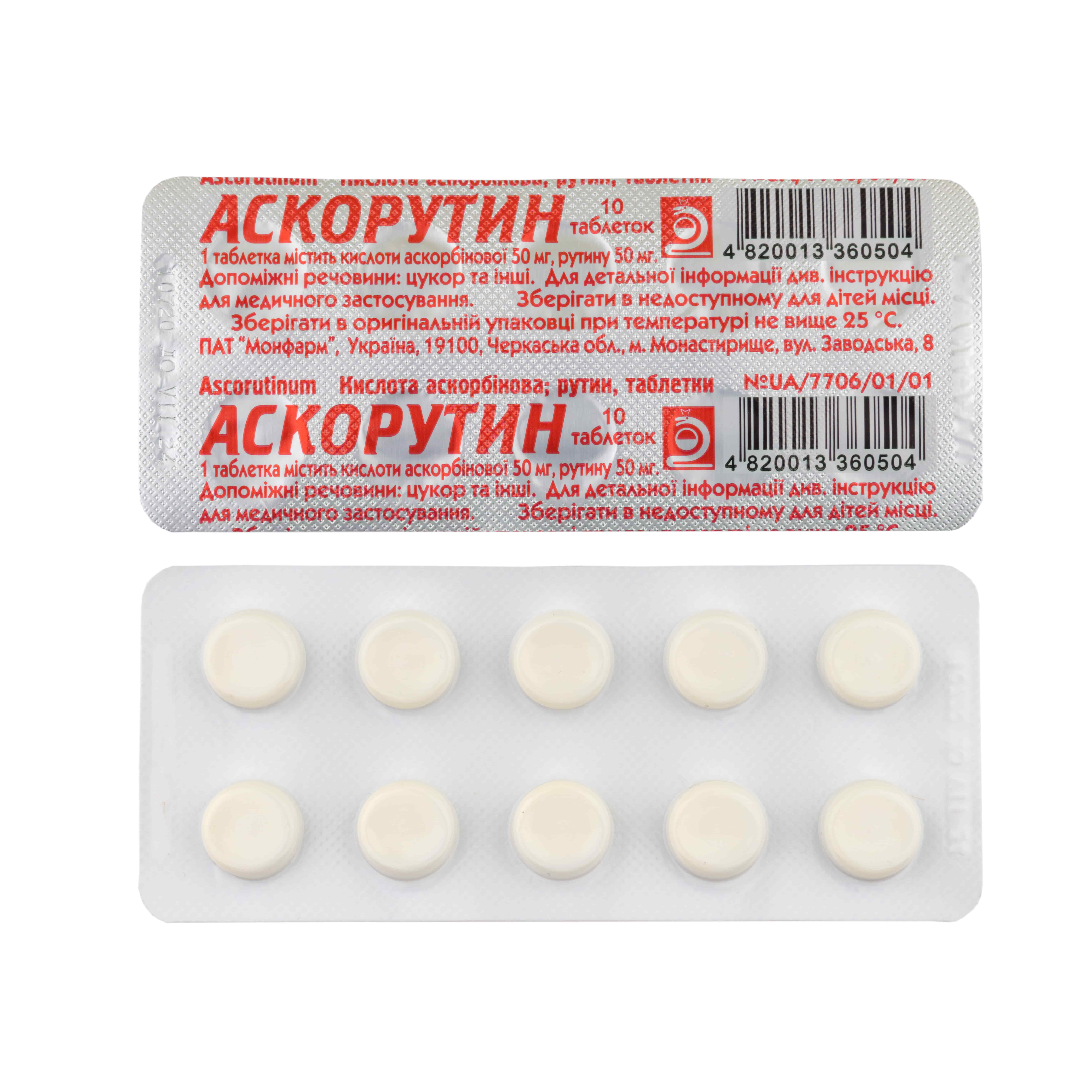
Release form
Tablets
For children
From 3 hroks
For pregnant women
Not recommended
For nursing mothers
Not recommended
For drivers
Does not affect
Storage temperature
to 25 °C
INSTRUCTION
storage
active substances: ascorbic acid; routine; 1 tablet contains ascorbic acid 50 mg, rutin 50 mg; auxiliary substances: potato starch; sugar; calcium stearate; talc.
Medicinal form
Tablets. Main physico-chemical properties: tablets of light greenish-yellow color with minor inclusions, with a flat surface, beveled edges and a line.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Capillary stabilizers. Bioflavonoids. ATX code C05S A51.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics. Combined medicinal product, the action of which is determined by the effects of the components included in its composition. Rutin (vitamin P) promotes the transformation of ascorbic acid into dehydroascorbic acid and prevents further transformation of the latter into diketogulonic acid. Therefore, most of the effects of rutin are mediated by ascorbic acid. Rutin in combination with ascorbic acid reduces the permeability and fragility of capillaries, strengthens the cell wall, reduces platelet aggregation, has an anti-inflammatory effect (including by inhibiting the activity of hyaluronidase), exhibits antioxidant properties, participates in redox processes. In addition, rutin has such effects as reducing the exudation of the liquid part of the blood plasma and the diapedesis of blood cells through the vascular wall; choleretic and mild antihypertensive effects. In patients with chronic venous insufficiency, rutin leads to a reduction in edema and pain syndromes, trophic disorders, reduction or disappearance of paresthesias and seizures. Helps reduce the severity of side effects of radiation therapy (cystitis, enteroproctitis, dysphagia, skin erythema), and also slows down the progression of diabetic retinopathy. Pharmacokinetics. Each vitamin included in the preparation undergoes its own transformations. Ascorbic acid is quickly absorbed mainly in the duodenum and small intestine. 30 minutes after intake, the content of ascorbic acid in the blood increases noticeably, its uptake by tissues begins, while it first turns into dehydroascorbic acid, which penetrates through cell membranes without energy expenditure and is quickly restored in the cell. Ascorbic acid in tissues is contained almost exclusively intracellularly, it is determined in three forms - ascorbic acid, dehydroascorbic acid and ascorbic acid (bound ascorbic acid). It is unevenly distributed between organs. A lot of it is contained in the glands of internal secretion, especially in the adrenal glands, less in the brain, kidneys, liver, heart and skeletal muscles. The content of ascorbic acid in leukocytes and platelets is higher than in blood plasma. It is metabolized and excreted up to 90% by the kidneys in the form of oxalate, partly in free form. Rutin, being absorbed in the digestive tract, contributes to the transport and deposition of ascorbate. It is excreted unchanged and in the form of metabolites, mainly with bile and to a lesser extent with urine. The half-life is 10–25 hours.
Indication
– Deficiency of rutin and ascorbic acid. - Diseases accompanied by increased permeability of blood vessels - as part of complex therapy. – To prevent colds and reduce flu symptoms. - To increase immunity.
Contraindication
Increased sensitivity to the components of the drug. Increased blood coagulation, thrombophlebitis, tendency to thrombosis; diabetes; gout, urolithiasis with the formation of urate stones, cystinuria, hypokalemia and hypercalcemia, oxalaturia; severe kidney diseases; simultaneous use with sulfonamides or aminoglycosides; fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Acetylsalicylic acid, oral contraceptives: decrease in drug absorption. Ascorbic acid in a dose of ≥1 g increases the bioavailability of oral contraceptives (estrogens, including ethinyl estradiol), increases the concentration of salicylates in the blood, increasing their side effects (risk of crystalluria, effect on the gastric mucosa). Acetylsalicylic acid, barbiturates, tetracyclines: increased excretion of ascorbic acid with urine. Penicillin (including benzylpenicillin), tetracycline, iron preparations: high doses of ascorbic acid can increase their absorption and concentration in the blood. Desferrioxamine (deferoxamine): increases the absorption of iron, its excretion with urine; tissue toxicity of iron increases, especially cardiotoxicity, which can lead to decompensation of the circulatory system. Cardiac dysfunction (usually reversible after withdrawal of vitamin C) has been reported in patients with idiopathic hemochromatosis and thalassemia treated with desferrioxamine and high doses of ascorbic acid (greater than 500 mg per day). Such a combination requires caution and careful monitoring of cardiac function in this category of patients. Ascorbic acid can be taken only 2 hours after the injection of desferrioxamine. Heparin, indirect anticoagulants, phenothiazines, fluphenazine, sulfonamide drugs, antibiotics of the aminoglycoside group: reducing the effectiveness of these drugs. Cyclosporin A: its bioavailability may decrease. Vitamins of group B: mutual strengthening of the therapeutic effect. High doses of ascorbic acid affect the resorption of vitamin B12. Corticosteroids, paracetamol: the half-life of the latter increases when high doses of ascorbic acid are used (this interaction has no clinical consequences when taking therapeutic doses). Calcitonin: the rate of absorption of ascorbic acid increases. Amphetamine: its renal excretion increases with the use of high doses of ascorbic acid. Aluminum antacids: it should be taken into account that ascorbic acid promotes the absorption of aluminum from the intestines, it is possible to increase the elimination of aluminum with urine. The combined use of antacids and ascorbic acid is not recommended, especially in patients with renal failure. With long-term use (more than 4 weeks), the drug should not be prescribed simultaneously with cardiac glycosides, antihypertensive agents or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, as it can increase their effect. Ascorbic acid increases the excretion of oxalates in the urine, thus increasing the risk of formation of oxalate stones in the urine. The combined use of very high doses of ascorbic acid with amygdalin (complementary medicine) may increase the risk of cyanide toxicity. Smoking, alcohol reduce the concentration of ascorbate in blood plasma. Disulfiram: Long-term intake of large doses of ascorbic acid inhibits the disulfiram-alcohol reaction. Ascorbic acid in large doses (more than 2 g/day) can affect the results of biochemical determinations of creatinine levels, uric acid and glucose in blood and urine samples, to determine the level of inorganic phosphates, liver enzymes and bilirubin in the blood. A stool screening test for occult blood may be falsely negative. Simultaneous use with alkaline drinking, consumption of fresh fruit or vegetable juices reduces the absorption of ascorbic acid.
Features of use
Simultaneous use of the drug with alkaline drinks, fresh fruit or vegetable juices reduces the absorption of vitamin C. Absorption of ascorbic acid can be disturbed in case of intestinal dyskinesias, enteritis and achilles. Since ascorbic acid increases the absorption of iron, its use in high doses can be dangerous for patients with hemochromatosis, thalassemia, polycythemia, leukemia and sideroblastic anemia. Patients with a high content of iron in the body should use the drug in minimal doses. Ascorbic acid should be used with caution in the treatment of patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, patients with a history of kidney disease. With long-term use of high doses of ascorbic acid, kidney function, blood pressure level, and pancreatic function should be monitored. With urolithiasis, the daily dose of ascorbic acid should not exceed 1 g. Do not prescribe large doses of the drug to patients with increased blood coagulation. Since ascorbic acid has a mild stimulating effect, it is not recommended to take the medicine at the end of the day. Due to the content of ascorbic acid in the medicinal product, it can change the results of a number of laboratory tests (see the section "Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions"). The drug contains sugar, which should be taken into account by patients with diabetes. Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding. During pregnancy, the drug can be used only as prescribed by a doctor. The drug is contraindicated in the first trimester of pregnancy. In the II-III trimesters of pregnancy or during breastfeeding, the drug should be prescribed taking into account the benefit/risk ratio for the woman and the fetus/child, provided that the recommended doses and duration of treatment are strictly followed. According to the available clinical data on the use of rutin and vitamin C in the form of individual medicines by pregnant women, no significant risks for the fetus were found. However, appropriate and well-controlled clinical studies of the safety of the use of combined preparations containing vitamin C and rutin in pregnant women have not been conducted. There are no reports of embryotoxicity of rutin or its penetration into breast milk. Vitamin C is excreted in breast milk, but doses even 10 times higher than the recommended daily dose did not lead to a significant increase in its concentration in breast milk. The ability to influence the speed of reaction when driving vehicles or other mechanisms. There is no data on the effect of Askorutin on the ability to drive vehicles or work with other mechanisms.
Methods of application
The drug should be administered orally after meals. Tablets should be swallowed whole with a small amount of water. For therapeutic purposes, adults are prescribed 1 tablet 2-3 times a day; children over 3 years old - 1 tablet 2 times a day. As a preventive measure, it is recommended to take the drug: adults - 1 tablet 2 times a day, children aged 3 years and older - 1 tablet 1 time a day. The duration of the treatment course is 3–4 weeks, depending on the nature of the disease and the effectiveness of the treatment. Children. The drug should be prescribed to children over 3 years of age.
Overdose
Symptoms: pain in the epigastric area, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, itching and skin rashes, increased excitability of the nervous system, headache, increased blood pressure, blood clots. It is possible to increase the manifestations of adverse reactions. Overdose can lead to changes in the renal excretion of ascorbic and uric acids during acetylation of urine with the risk of precipitation of oxalate stones. With long-term use in large doses, suppression of the function of the insular apparatus of the pancreas, impaired kidney function is possible. Ascorbic acid in doses exceeding 3 g/day may cause acidosis or hemolytic anemia in some individuals with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. Treatment: gastric lavage, use of sorbents, symptomatic therapy.
Side effects
From the side of the central nervous system: headache, feeling of fatigue, with long-term use in high doses - sleep disturbance, increased excitability of the central nervous system. On the part of the kidneys and urinary tract: acidification of urine, hyperoxalaturia in patients of the risk group at doses exceeding 1 g/day; with long-term use in high doses - damage to the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys, formation of urate and oxalate stones in the urinary tract, kidney failure. Doses of ascorbic acid over 600 mg/day have a diuretic effect. From the side of the blood system: with long-term use in high doses - thrombocytosis, hyperprothrombinemia, thrombus formation, erythrocytopenia, neutrophilic leukocytosis, hemolytic anemia in some individuals with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. From the side of metabolism: hypervitaminosis C, deterioration of tissue trophism, with long-term use in high doses - suppression of the function of the insular apparatus of the pancreas (hyperglycemia, glucosuria) and glycogen synthesis, sodium and fluid retention, impaired zinc and copper metabolism. From the side of the cardiovascular system: with long-term use in high doses - myocardial dystrophy, increased blood pressure, development of microangiopathy. From the side of the digestive tract: with long-term use in high doses - irritation of the mucous membrane of the digestive tract, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea. From the side of the immune system: hypersensitivity reactions, including skin hyperemia, skin rashes, eczema, itching, Quincke's edema, urticaria, anaphylactic shock, respiratory hypersensitivity reactions.
Expiration date
4 years.
Storage conditions
Store in the original packaging at a temperature not higher than 25 ºС. Keep out of the reach of children.
Packaging
10 tablets in a blister. 10 tablets in a blister; 2 blisters in a pack. 10 tablets in a blister; 5 blisters in a pack. 10 tablets in a blister; 10 blisters in a pack.
Leave category
Without a prescription.
Producer
Monfarm PJSC.
Address
Ukraine, 19161, Cherkasy region, Uman district, village Avramivka, str. Zavodska, 8.
